
Virtual Servers Explained – How Virtual Servers Work
Everything can be done on the internet nowadays. From simple browsing to online transactions, we’re not even sure how we did things anymore before the internet came to be. But while we know that servers are the backbone of the internet, many of us are not sure about the new thing called virtual servers. Virtual servers are precisely like physical servers, but the difference lies in how the processing power of physical servers is utilized.
What are Virtual Servers
Traditional servers tend to take up at least one physical server each. While this makes maintenance simple and operations streamlined, costs become higher because the processing power of the server is only utilized towards one application or platform. And physical servers aren’t really “cheap” to buy and maintain either as they tend to be expensive devices that eat up a lot of electricity. But with physical servers becoming more efficient in terms of storage and processing power, some data centers have decided to insert two or more applications in one server via a hypervisor that emulates the capabilities of multiple physical servers in one. This is how virtual servers came into existence.
Purpose of Virtual Servers
The functions of virtual servers are various depending on their application. Some of the basic functions include web hosting, as well as data storage and app hosting. But since hypervisors emulate physical hardware as well, each virtual server also comes with a virtual CPU, virtual memory, virtual disks, a virtual networking interface, and an operating system along with the existing hardware of physical servers. Computer scientists categorized these functions under the term “Infrastructure as a Service” (IaaS). Though virtual servers are a form of IaaS, they are often mistaken for cloud servers which have a similar function but with different methods of operation.
Due to their digital nature, virtual servers are usually the priority choice for testing new software, applications, and operating systems. This is because of the highly customizable nature of virtual servers, and their openness to customization. Computer scientists and tech engineers may use virtual servers to implement new programs, and even test viruses, that may damage existing machine hardware.
Considering the independence of virtual servers from their physical device, they are also often used by companies or users as back up storages in case that original copies of their programs are erased. They may also use virtual servers to transfer legacy applications or programs that are no longer supported due to their outdated nature. Virtual servers may emulate hardware that is no longer supported, allowing users to use old programs and applications to their pleasure.
Advantages of Virtual Servers
One advantage of Virtual Servers is its portability. Considering that it is a series of programs that mimic hardware, and not necessarily hardware itself, virtual servers can be transferred to one physical device to another if there is a need that arises from it. This also means that it is much easier to back up virtual servers, and if the original copy of the virtual server is wiped out – a backup copy can be used in its stead. Virtual servers are independent of their physical device, and any back up can be installed in any machine that can run it.
Virtual servers can also be customized heavily, similar to any other dedicated server. Users have direct access to the operating system and server software. This means that users not only can customize their apps or website hosted in a virtual server but also how the server operates in terms of processing and power consumption. Some limits can be imposed however intentionally by data centers with regards to safety and security. Since virtual servers have dedicated processing and storage, they tend to have high performance. Power management can be managed so that if resource consumption for processing is low, this could be utilized in order to lower electricity costs.
Existing virtual servers may also use several security requirements, tools, and operating systems in order to reduce vulnerabilities. In worst cases, virtual servers may be isolated from one another to prevent vulnerabilities from other virtual servers from affecting the entire infrastructure of the physical device. Existing space requirements of the physical device may be configured for optimal storage of several virtual servers. This can also improve boot up time and make processing of programs more efficient as well.
Disadvantages of Virtual Servers
Though virtual servers have dedicated processing power, this is still limited to the extent of the capacity of the physical server. This is also considered especially since there are various virtual servers that are stored in the same physical device. This may also affect scalability as an unexpected surge in traffic might overwhelm the number of server resources dedicated to your hosted program. Issues may arise as there are no existing methods to measure the performance of virtualized environments. Adding an extra layer of software via the hypervisor may be the closest in measuring performance, but this will be done at a higher processing cost which could also affect the quality of service for the existing physical device.
Security may become an issue. Though virtual servers have safeguards similar to dedicated servers, security risks from other virtual servers within the same physical device may affect your own as well in the assumption that they are not isolated from one another. Management of virtual environments may become tedious as a consequence of its customizability. Virtual servers will need to be constantly monitored, configured and saved though there are products available in the market to make these practices convenient.
Different Types of Virtual Servers
Various Virtualization methods exist right now, which creates different forms of virtual servers depending on the function of the application, the requirement of users, as well as other factors. They are usually marketed as IaaS in the existing marketplace. One type of virtual server focuses on operating systems where they are moved into a digital environment. The operating system operates like any other with the exemption that all of its processes do not rely on existing hardware to run. Because the operating system is virtualized, this also means that they can be portable and even be moved or transferred via USB.
Of course, traditional physical servers themselves can be transferred to virtual servers. So instead of just emulating one program, application, or operating system, an entire server is digitalized so that more virtual servers can be included in the physical device. It is also possible to transform traditional physical servers into cloud servers, though the differences between virtual vis-à-vis cloud will be discussed later on.
As an emulation tool, virtual servers can also mimic hardware akin to its original functions. This is essential particularly for legacy devices that are no longer supported by companies. A virtual server can mimic old PCs, gaming consoles, and other hardware separated from the actual physical device. Moreover, virtual servers emulating hardware are also used for testing and diagnosis to measure the performances and limits if said devices in the digital realm.
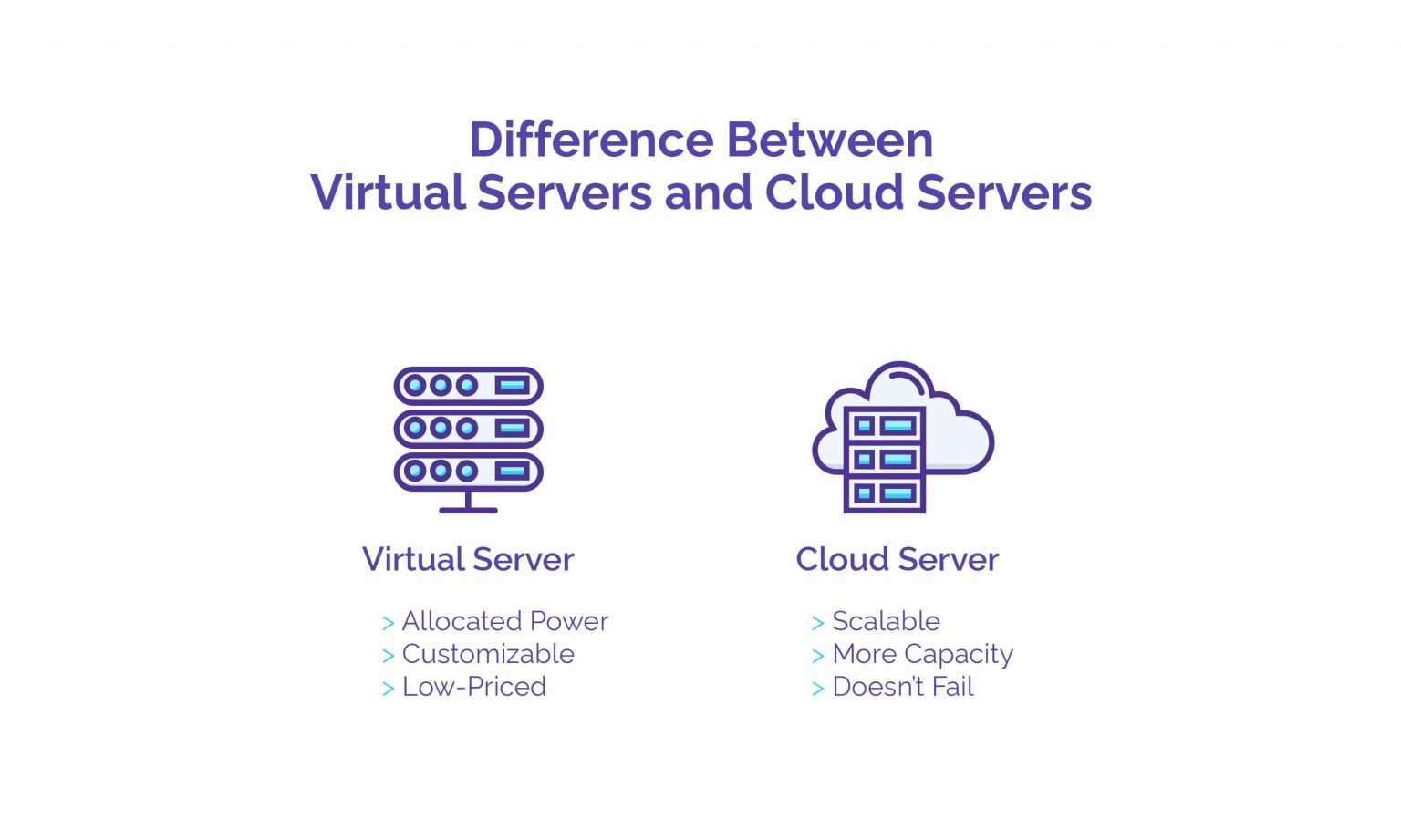
With the rise of cloud computing, physical servers can share processing power to form several cloud servers in order to provide services at a reduced cost. This sharing of space and processing power in the digital realm is what differentiates between virtual servers and cloud servers. Whereas virtual servers share one physical server, cloud servers use different physical servers in sharing processing power.
In terms of scalability, cloud servers have the advantage of adding more capacity in real time as additional sources of processing power can be added by connecting to new physical devices. Virtual servers, as mentioned previously, will have to rely on the allocated processing power by a single physical device. For customizability, cloud servers have the addition of tweaking network architecture, firewall, and IP addresses as it exists via connections from different physical devices. But this same infrastructure may limit cloud server customizability depending on the permissions granted by several physical devices. Since virtual servers act like dedicated servers, they tend to be more convenient in terms of customizability.
Security may be a concern for cloud servers. Though they are still high in terms of safeguards, their nature of being continuously connected on the internet means that they are more vulnerable to cyber-attacks compared to virtual servers. The advantage of cloud servers, however, is due to its decentralized nature, it has no single point of failure as compared to virtual servers.
Costing is cheaper for virtual servers mainly due to limited processing capacity. Cloud servers are also cheap compared to traditional servers; but because they are always connected to the web, the payment plans offered are usually on a pay-per-use system. Traffic spikes may increase cloud server costs unless managed otherwise.
With that being said, it is also possible for virtual servers to be converted into cloud servers and vice versa. It all depends on user preference and the function of the existing program, application, or website. Cloud servers may be preferable for applications such as social media that expect continuous growth but are not allowed to crash at least once. But if a user gives more premium on stability and customizability, virtual servers are the way to go.
Virtual Server Software Available
Several virtual servers are available in the market right now at the pleasure of users and clients. These include Microsoft Virtual Server, Virtual Box, VMware Server, Microsoft Azure, and Amazon Elastic Compute. Microsoft Azure, for instance, offers both virtual server and cloud server products as part of their IaaS platforms. They are usually helpful for building, testing, and managing applications with effective scalability. Microsoft Azure is hosted on existing Microsoft data centers and offers both closed source and open source licenses. Virtual machines, app services, website hosting, storage, and even mobile services are just some of the available uses for Microsoft Azure.
Amazon Elastic Compute is similar in terms of providing both cloud and virtual servers. Amazon Elastic Compute is part of the Amazon Web Services platform for IaaS products. It allows launching of virtual servers with customizable security, as well as data storage needs. Scalability is also a feature especially with regards to web traffic, to which its virtual servers and cloud servers can be scaled up or down to reduce the need to forecast traffic. Applications and web hosting are available under Amazon Elastic Compute, with different payment options ranging from on-demand instances, reserved instances, and spot instances.
Virtual Box is a hypervisor owned and operated by the Oracle Corporation. It is essentially a free and open source hypervisor and can be installed on a variety of operating systems including Linux and Windows. Virtual Box is a type of virtual server that’s focused more on hardware and operating system Virtualization. This allows users to emulate various types of operating systems and hardware in powerful desktop computers and even laptops. Virtual Box can also emulate ethernet network adapters without the need to find and install respective drivers for user convenience.
Conclusion on Virtual Servers
Users often cite the appeal of virtual servers for a variety of reasons, including its existing redundancies, scalability, security, and emulation. Concerning redundancy, users can virtualize additional servers without the need for spending on extra cash to purchase new physical devices. This not only means additional revenue but also less interruption and downtime for services. For scalability, users can utilize virtual servers and consolidate them on a single physical device.
Moreover, they may customize dedicate processing power, existing virtual hardware, and processes. Security and safeguards may also be tweaked depending on user preference or program function. Of course, the opportunity of virtualizing legacy hardware can be useful for businesses that will make the transition to new hardware more convenient.
Virtual servers are part of a new trend of IaaS that is becoming more foundational in businesses. It is no secret that the largest tech companies such as Microsoft and Amazon are offering virtual servers as a core part of their business services. This makes virtual servers more integral with business demands, as with several clients relying on it to host websites or experiment with new programs.



