
The virtual private server, or VPS, has become one of the most popular web hosting products in recent years. VPS allow customers to have full root access to their servers, which makes them great for hosting resource heavy websites, VPNs, game servers, and thousands of other applications.
One stumbling point for customers is the choice between OpenVZ vs KVM. Many web hosts offer the option between OpenVZ VPS and KVM VPS, but the differences between the two technologies often go overlooked. Before going into any depth of the pros and cons of OpenVZ vs KVM VPS difference, it is important to first get a general sense of what the virtualization technology is and what the limitations are for each.
OpenVZ: Container-based Virtualization
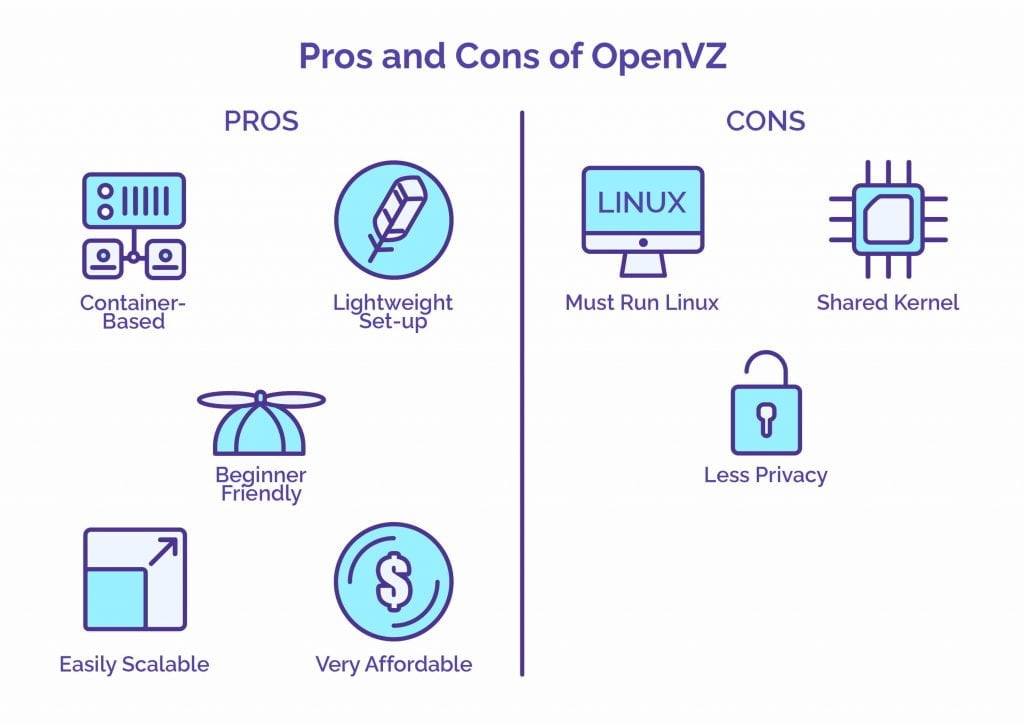
OpenVZ VPS Hosting is container-based. There are a few key results of container-based virtualization. They are that OpenVZ resources are not fully guaranteed, that web hosts can see the individual processes and files running on your VPS, and that the shared kernel results in issues supporting certain operating systems and applications.
Resource Allocations & Overselling
OpenVZ VPS do not have fully guaranteed resources. Instead, resources are shared with other VPS on the same physical server, with each VPS having individual limitations for how much memory, bandwidth, CPU, and disk space can be used. The lack of fully guaranteed resources is not an issue for most users, but it is important to note that OpenVZ VPS can be oversold. However, KVM VPS can also be oversold, so there is no way to ensure that VPS are not being oversold, except for asking your web host. Many web hosts will be forthcoming about this information.
Privacy
OpenVZ VPS also lack a certain degree of privacy. One factor in this is that web hosts can see the individual processes that are running on OpenVZ Servers. This is not of concern for most users, but the most privacy conscious may prefer to have a private environment. Another factor causing the lack of privacy is the fact that web hosts can see the files that are stored on an OpenVZ VPS, and that there is no way to encrypt the hard drive or its contents. KVM, on the other hand, offers both encryption and hides the individual processes that your VPS is running.
One final consequence of importance is that all OpenVZ VPS are forced to share the same kernel. In most cases, this is not an issue, but the result of this limitation is that only Linux can be hosted on OpenVZ. The other limitation to sharing a kernel is that custom kernel modules cannot always be enabled due to the shared OpenVZ Kernel. For instance, there is only limited support for programs like Docker on OpenVZ.
Conclusion
With OpenVZ Servers, however, it is not all cons. Some of the pros to this virtualization technology include the fact that it is incredibly lightweight, easy to set up, and offered at great prices.
KVM: Full Virtualization
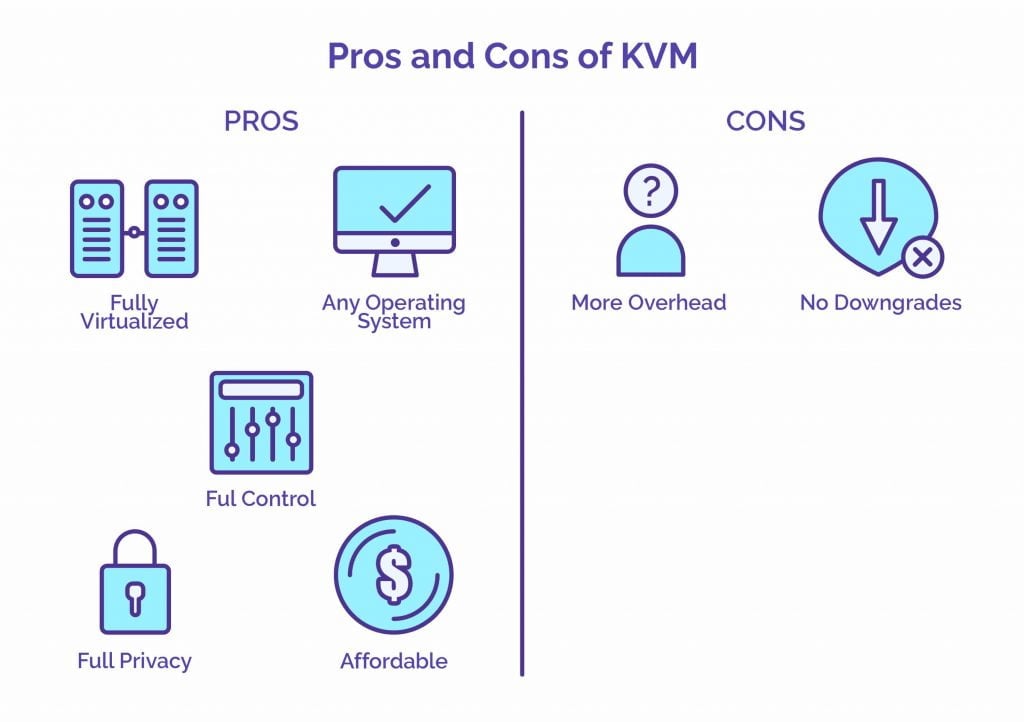
KVM VPS Hosting is fully virtualized. The differences from OpenVZ VPS is that it supports custom kernels and kernel changes, has better privacy, and the fact that resources are fully allocated to each VM. KVM has earned a reputation in the web hosting industry for being of a higher quality than OpenVZ, and these differences generally detail why that has become the case.
Resource Allocations & Overselling
KVM VPS cannot be readily oversold. Overselling is still possible with KVM, but there are hard limitations in place that make this practice difficult. The resources that are allocated to a KVM VPS are fully allocated, and they cannot be used for other servers (in rare cases, web hosts do oversell their KVM VPS, but this is a relatively uncommon practice).
Privacy
KVM technology also has full support for hard disk encryption. This means that no one can see the files on your VPS, even if they try, unless they have the root password. This factor alone makes KVM one of the most secure Virtualization technologies available.
Dedicated Kernel
KVM actually stands for kernel-based virtual machine, which explains the fact that each virtual machine has its own kernel. With a KVM VPS, the user can do whatever they want to the kernel within the server. In fact, it is even possible to run OpenVZ on top of KVM (it is not possible, however, to run KVM on top of OpenVZ).
Conclusion
KVM VPS Hosting is not always perfect, though. KVM VPS can be more expensive to run, they require more resources than their OpenVZ counterparts, and operating systems must be manually installed in certain cases.



17 Replies to “OpenVZ vs KVM VPS – What is the Difference? – Virtualization Explained”